What You Need to Know
ABOUT UTIs

A urinary tract infection (UTI) is when bacteria gets into your urine and travels up to your bladder.
About


&
will have symptoms of at least
1 UTI during their lifetime.


Symptoms of a UTI can include:
- Pain or burning when you pass urine.
- Urine that looks cloudy or smells bad.
- Pressure in your lower stomach.
- An urge to go to the bathroom often.
UTIs often occur among young women during puberty and after menopause.
About 1 in 5 young women who have a UTI will have another.
To prevent a UTI, you should:
Urinate after sex to flush out bacteria that may have gotten into the urinary tract during intercourse.
Drink plenty of fluids to keep well hydrated.
Not put off urinating when you need to and don’t rush to finish.
Wipe from front to back to keep bacteria around the anus from getting into the vagina or urethra.
UTIs are the second most common type of infection in the body and are the reason for more than
8 million visits to the doctor each year.

Most UTIs are not serious, but some can lead to serious problems, like kidney infections.
Most UTIs in women can be treated with a short course of antibiotics (usually three days). Some infections need to be treated for five days.
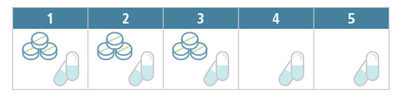

Keep taking your medicine even after you start feeling better. Unless UTIs are fully treated, they can often return.
For more information on UTIs, visit the Urology Care Foundation’s website: UrologyHealth.org
UrologyHealth.org | WINTER 2017/2018 | UROLOGYHEALTH extra